Design, Synthesis and Functionalization of Nanomaterials...
GC001B-14SBS: Design, Synthesis and Functionalization of Nanomaterials with Raman and Biomolecular Fingerprint for Biosensor and Microarray Integration
Abstract:
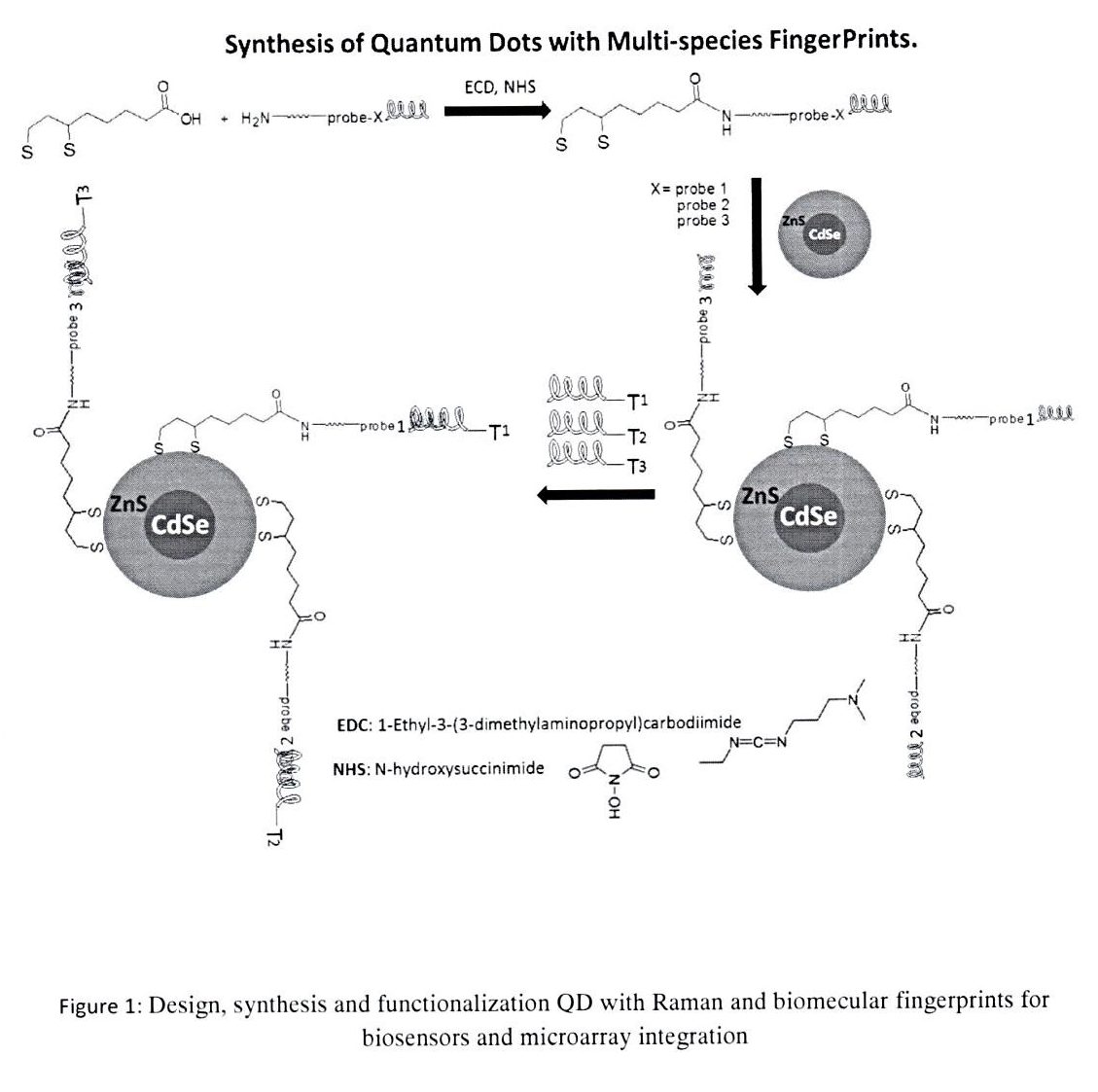
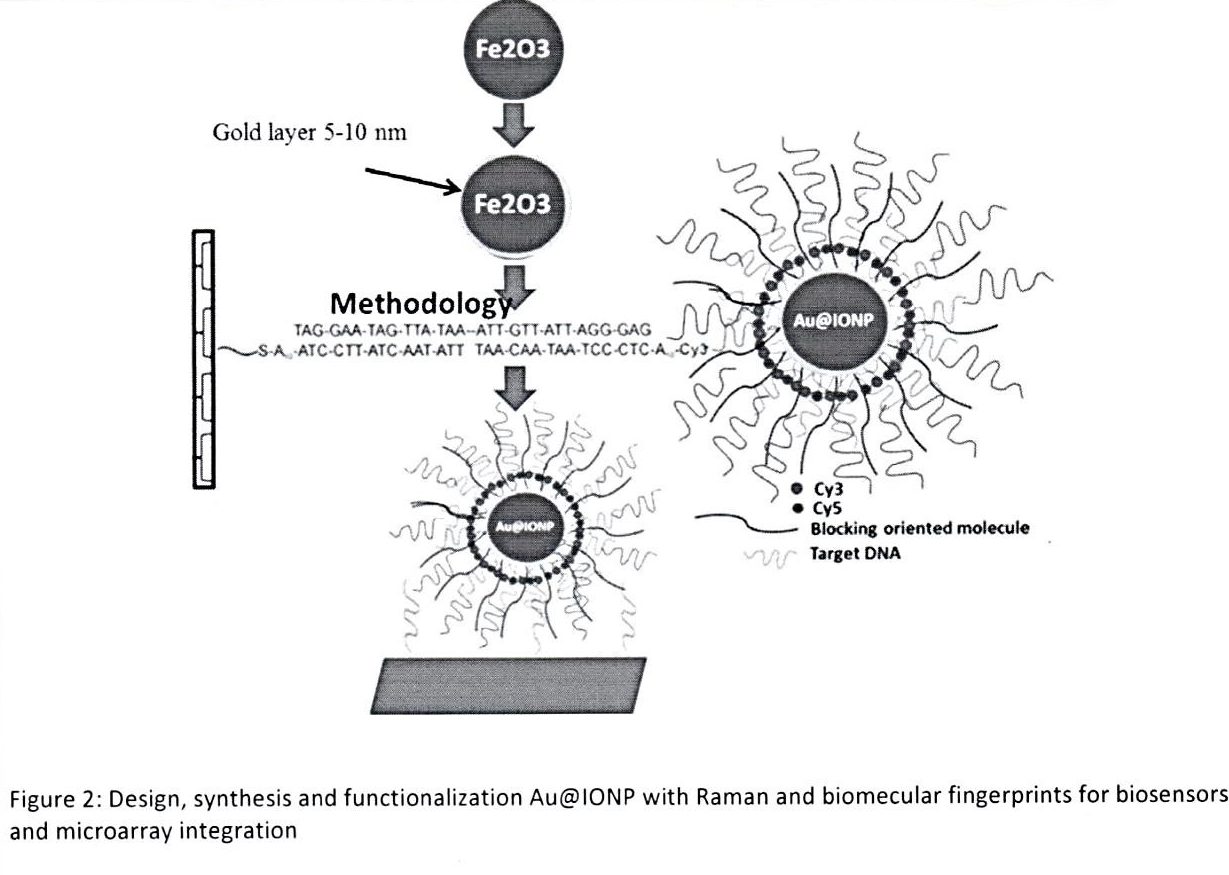
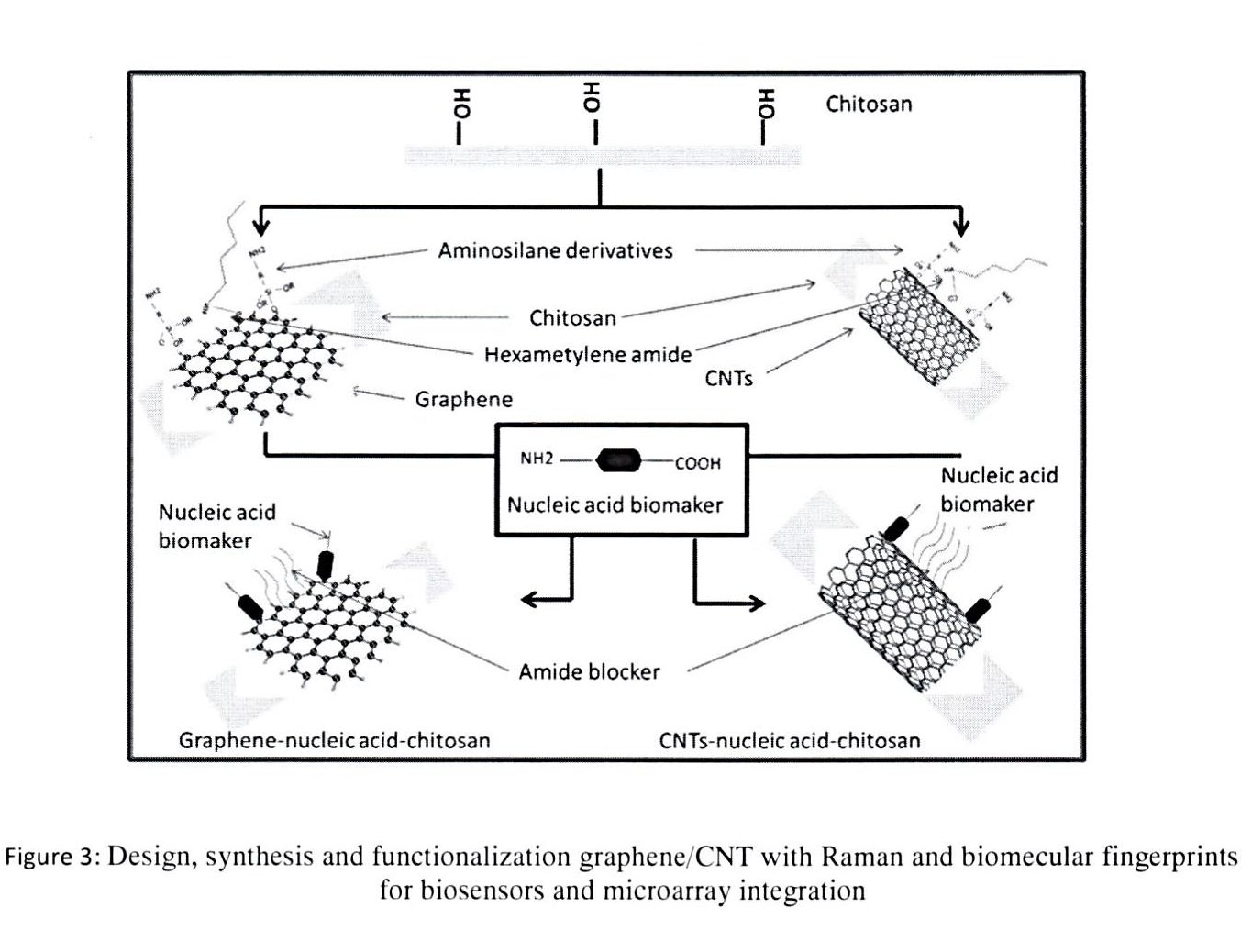
Labelling of biological molecules using fluorescent tags is a common and very useful practice in biological science. Fluorescent small molecules (organic dyes) are used in both single and multiplex detection approaches. However, tagging of biomolecules using organic fluorophores has significant limitations. Organic fluorophores tend to have narrow excitation spectra, and often exhibit broad emission band with red tailing, which makes simultaneous quantitative evaluation of relative amounts of different probes present in the same sample difficult, due to spectral overlap. Quantum dots (QDs), have the potential to overcome problems encountered by organic small molecules in certain fluorescent tagging applications. The using of iron oxide and gold within the one system (Au@IONs), a multifaceted system can be developed which exploits the surface chemistry of the gold whilst retaining the magnetic character of the iron oxide. Recently, electrochemical properties of carbon nanotubes (CNT) and graphene have been unveiled, and their application towards electrochemical sensors and biosensors has gained interest. Functional graphene and CNT have been proposed in the development of electrochemical nucleic acid biosensor. Most of the graphene sensing research focused on the utilizing of only native graphene to promote electron-transfer reactions with electro-active species. Therefore, aminosilane derivative proposed to use as dispersion and surface modification agent. This research is to assemble oligonucleotides and Raman labels on QDs, Au@IONP grapheme and CNT which could be a highly efficient way to enhance multiplexed detection of oligonucleotides targets. Cy3, Cy5 and Cy7 (Raman active dyes) are the most popular cyanine dyes, used typically combined for 3 color detection. Accordingly, we hypothesize that the assembly of nanomaterials labeled with oligonucleotides, Raman active dyes (Cy3, Cy5 and Cy7) and blocking oriented monolayers of alkyl mercaptans which could provide the possibility of improving new system of QD, Au@IONPs, graphene and CNT with Raman spectroscopic fingerprints for DNA and RNA detection. The aim of this study is to validate this hypothesis and to use this nanoengineering technique to develop a novel multiplexed detection of oligonucleotides targets to achieve a highly sensitive and selective detection format for DNA. The Raman spectroscopic fingerprint, which will be designed through three Raman labels. QD, Au@IONP, graphene and CNT modified with Cy3, Cy5 and Cy7 labeled, alkyl thiol-capped oligonucleotide strands will be used as probes to monitor the presence of specific target DNA strands.
Research Objectives:
To synthesis functionalized nanomaterials with Raman and biomolecular fingerprints.
Methodology:
-
Synthesis of nanomaterials: oxide nanoparticles, gold coated iron oxide, graphene oxide and CNTs.
-
Functionalize of QD and Au@IONP and Graphene/CNT with Biomolecular Fingerprints for DNA and RNA detection.
Sub-programme Leader
Dr Wageeh AbdulHadi Yehya
Co-Researchers
Dr Nurhidayat Ullaili Binti Muhd Julkapli, Prof Dr Sharifah Bee, Dr Samira Bagher, Assoc. Prof Dr Md Eaqub Ali & Prof Dr Wan Jeffery Basirun
Outputs:
ISI-Indexed Journals